RBD
RBD – Reliability Block Diagram with Monte-Carlo simulation
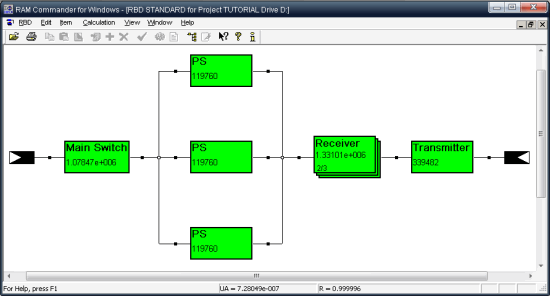
RBD-supported configurations
• Series
• Parallel
• K-out-of-N with active (hot) redundancy
• K-out-of-N with stand-by (cold) redundancy
• Partially loaded K-out-of-N – warm redundancy
• K-out-of-N w/repair, w/o repair, w/restricted repair
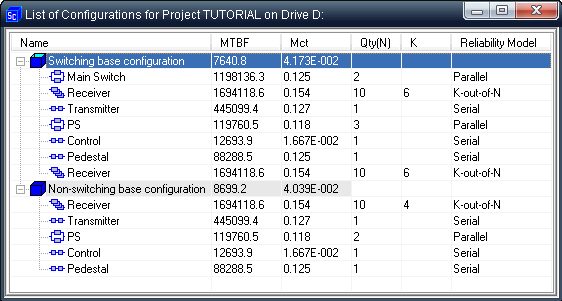
• K-out-of-N with Switch
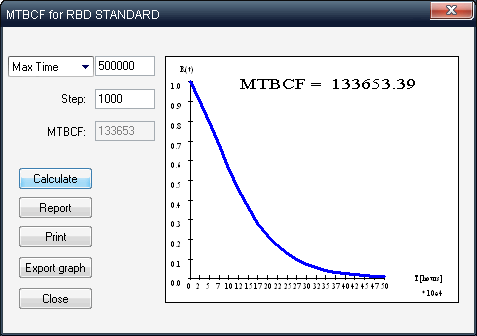
• Sub-RBD, K-out-of-N for Sub-RBDThe analytical technique is used mostly for exponential distributions. For each RBD, a graph of the reliability function R(t) can be drawn and MTBCF (Mean Time Between Critical Failures) can be calculated using numeric integration.Monte Carlo simulation with its’ high speed, accuracy, and large number of steps allows to evaluate Reliability and Availability for arbitrary configurations when there is no analytical solution, i.e. complex configurations, including standby, partially loaded and active redundancy; full or restricted repair with non-exponential distribution of time-to-repair; analysis under non-steady, transient state; dependent RBD elements; analysis of periodical inspection policy.
Distributions
- Exponential
- Normal
- Log-Normal
- Weibull
- Erlang
- Uniform